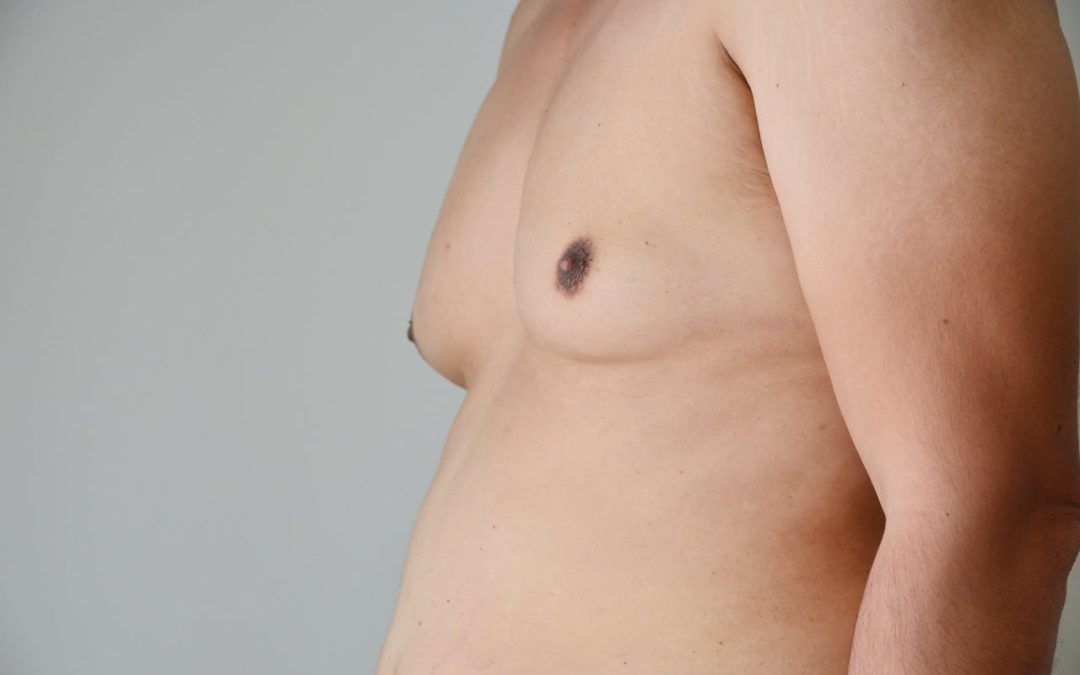
Chest fat, also known as adipose tissue, can exist in various forms in the chest area. In males, excess fat might result in gynecomastia, causing breast tissue enlargement due to hormonal imbalances or obesity. This is a common aesthetic concern. In females, chest fat is normal and contributes to mammary tissue and hormonal functions. Balancing chest fat through exercise, diet, and hormonal regulation is essential for maintaining health and positive body image in both genders.
The Two Different Forms of Chest Fat
Chest fat exists in two primary forms: subcutaneous and visceral fat. Subcutaneous fat is found just beneath the skin’s surface and contributes to body shape and insulation. In the chest area, excess subcutaneous fat can lead to gynecomastia in males and influence breast size in females. Visceral fat, on the other hand, surrounds internal organs and poses greater health risks, such as cardiovascular diseases. Balancing these fat types through healthy lifestyle choices is crucial for overall well-being.
Causes of Excessive Chest Fat
Excessive chest fat can be attributed to various factors:
1. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances, such as elevated estrogen levels and decreased testosterone, can disrupt the normal fat distribution in the body. In males, this can result in the accumulation of chest fat, a condition known as gynecomastia. Excessive estrogen can stimulate breast tissue growth, leading to an enlarged appearance. Hormonal fluctuations can also impact metabolic processes, favoring fat storage in certain areas. Addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance through medical intervention or lifestyle changes can help mitigate chest fat accumulation.
2. Obesity
Obesity can contribute to chest fat accumulation through a combination of factors. Excess body fat can lead to hormonal imbalances, with increased estrogen and decreased testosterone levels, promoting the growth of breast tissue in males. Additionally, obesity often disrupts metabolic processes, favoring fat storage in various regions, including the chest. As fat cells expand, they can cause the chest area to appear enlarged. Managing obesity through healthy diet, exercise, and medical guidance can help reduce chest fat and its associated effects.
3. Genetics
Genetics can influence chest fat accumulation by determining factors like hormone levels, fat distribution patterns, and metabolic rates. Certain genetic variations may increase susceptibility to hormonal imbalances, like higher estrogen and lower testosterone, fostering breast tissue growth in males. Genetic predispositions can also affect where fat is stored, potentially leading to chest fat buildup.
4. Medications
Some medications can lead to chest fat accumulation by disrupting hormone levels or metabolic processes. For example, certain drugs might cause hormonal imbalances, like elevated estrogen, contributing to gynecomastia in males. Medications can also affect fat distribution, promoting fat storage in the chest area. It’s important to note that not all medications have this effect, and individual responses may vary.
5. Ageing
Ageing can lead to chest fat accumulation due to hormonal changes and shifts in metabolism. As men age, testosterone levels may decline while estrogen levels remain relatively stable, promoting the growth of breast tissue. Additionally, age-related decreases in metabolism can result in overall fat gain, including in the chest area. These factors combined can lead to an increase in chest fat.
6. Unhealthy Lifestyle
An unhealthy lifestyle, characterized by poor dietary habits and lack of physical activity, can contribute to chest fat accumulation. High-calorie diets and excessive consumption of processed foods can lead to weight gain and fat storage, including in the chest region. Sedentary behavior further compounds the issue by slowing down metabolism and reducing muscle mass. This combination of factors disrupts hormone levels, potentially causing gynecomastia. Additionally, unhealthy habits can increase stress, which might impact hormonal balance.
7. Medical Condition
Certain medical conditions can lead to chest fat accumulation. Conditions like hormonal imbalances, such as Klinefelter syndrome or hyperthyroidism, can disrupt testosterone and estrogen levels, promoting breast tissue growth in males. Metabolic disorders can influence fat distribution, favoring chest fat accumulation. Chronic conditions like liver disease can impact hormone processing, contributing to gynecomastia. Additionally, some tumors or genetic disorders might cause hormonal changes that affect chest fat.
Summary
Excessive chest fat can stem from hormonal imbalances, obesity, genetics, medications, aging, unhealthy lifestyles, and medical conditions. Factors such as disrupted fat distribution, hormone levels, and metabolism contribute to chest fat accumulation. Addressing these causes through interventions and lifestyle changes can mitigate chest fat development.
Health Implications of Excessive Chest Fat
1. Increases the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
Excessive chest fat, primarily linked to overall obesity, poses a heightened risk of cardiovascular diseases. The adipose tissue in the chest region contributes to a systemic inflammatory state, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia. These factors collectively foster the development of atherosclerosis, where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to plaque accumulation. This condition raises the likelihood of hypertension, coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Additionally, chest fat can be an indicator of visceral adiposity, which further exacerbates cardiovascular risks.
2. Impact of Self Esteem and Body Image
Excessive chest fat can significantly impact self-esteem and body image. In males, it can lead to gynecomastia, causing embarrassment, social anxiety, and feelings of self-consciousness. Body dissatisfaction stemming from chest fat can lead to avoidance of activities that expose the chest, affecting one’s social life and mental well-being. Individuals may experience lowered self-esteem, negative body image, and even depression. Struggling with body image issues can result in social isolation, reduced confidence, and reluctance to engage in physical activities.
3. May Cause Hormonal Imbalance
Chest fat can influence hormonal imbalance through adipose tissue’s ability to produce hormones and affect their metabolism. Adipose tissue can produce estrogen, and excess chest fat can lead to an overproduction of this hormone. Elevated estrogen levels relative to testosterone can disrupt the hormonal equilibrium, contributing to imbalances. Additionally, adipose tissue contains enzymes that can convert certain hormones, like androgens, into estrogen. This conversion can further skew hormone ratios. Hormonal imbalances, in turn, may stimulate more fat accumulation in the chest area due to increased estrogen’s effects on fat distribution. This interplay creates a feedback loop, where chest fat and hormonal imbalance reinforce each other.
How to Reduce Chest Fat Accumulation
Preventing chest fat involves a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and medical guidance:
1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in reducing chest fat by promoting overall weight loss and aiding hormonal balance. It provides essential nutrients while controlling calorie intake. Protein-rich foods support muscle growth and maintenance, which can boost metabolism and aid in fat loss. Complex carbohydrates offer sustained energy, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Incorporating healthy fats, like those from avocados and nuts, can help regulate hormone production.
Additionally, a balanced diet supports steady blood sugar levels, reducing cravings and preventing excessive calorie consumption. Hydration from water and fiber-rich foods can help control appetite. By addressing nutritional needs and creating a calorie deficit, a balanced diet supports gradual and sustainable chest fat reduction when combined with regular exercise and healthy habits.
2. Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is integral to reducing chest fat as it contributes to overall fat loss and enhances metabolic activity. Cardiovascular exercises like running, cycling, or swimming increase calorie expenditure, promoting a calorie deficit necessary for fat reduction, including in the chest area. Strength training exercises, focusing on chest muscles like push-ups and bench presses, help build lean muscle mass, which elevates resting metabolism and aids in fat burning.
Exercise also stimulates hormone production, supporting a healthier hormonal balance that can mitigate chest fat accumulation. Consistency is key; combining cardiovascular workouts with targeted strength training several times a week, along with a balanced diet, is an effective approach to achieving and maintaining a leaner chest.
3. Hydration
Hydration plays a role in reducing chest fat by supporting metabolism and controlling appetite. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain proper metabolic function, enhancing the body’s ability to efficiently use stored fat for energy. Additionally, staying hydrated can curb false hunger cues, preventing overeating and unnecessary calorie consumption. Water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables also contribute to a feeling of fullness. By staying properly hydrated, individuals can promote an environment conducive to fat loss, complementing other lifestyle factors like balanced nutrition and regular exercise for effective reduction of chest fat.
4. Stress Management
Effective stress management aids in reducing chest fat by regulating hormones and preventing emotional eating. Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, promoting fat storage, especially in the abdominal and chest areas. Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can lower cortisol production. Additionally, managing stress helps avoid emotional eating, where high-calorie comfort foods are consumed in response to stress, contributing to weight gain. By keeping cortisol levels in check and preventing unhealthy eating habits, stress management supports a healthier hormonal balance and reduces the likelihood of chest fat accumulation.
5. Adequate Sleep
Adequate sleep is crucial for reducing chest fat due to its impact on hormones and metabolism. Insufficient sleep disrupts hormones like ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite and satiety, potentially leading to overeating and weight gain, including chest fat. Proper sleep duration supports balanced hormone production, promoting optimal metabolic function and fat utilization. Moreover, sleep deprivation can elevate cortisol levels, promoting fat storage, particularly around the chest area. Prioritizing 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night fosters a healthier hormonal environment and metabolic rate, enhancing efforts to reduce chest fat when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
6. Consistency
Consistency is a key factor in reducing chest fat as it ensures sustained efforts towards healthy habits. Regular adherence to a balanced diet and exercise routine maintains a consistent calorie deficit necessary for fat loss, including in the chest area. Consistent exercise routines aid in building muscle mass, elevating metabolism, and enhancing fat-burning efficiency. By avoiding erratic changes and crash diets, the body’s hormonal balance remains more stable, which helps prevent fat storage. Consistency also prevents weight fluctuations that could exacerbate fat distribution issues. Long-term commitment to positive lifestyle changes ensures gradual and sustainable reduction of chest fat and overall body fat.
Summary
Preventing chest fat involves maintaining a balanced diet that aids weight loss and hormonal balance. Protein supports muscle growth, complex carbs provide steady energy, and healthy fats regulate hormones. Hydration controls appetite, while exercise boosts fat loss and metabolic activity. Stress management curbs cortisol-related fat storage. Adequate sleep regulates hormones and metabolism. Consistency in diet and exercise sustains a calorie deficit, muscle growth, and hormonal balance. This holistic approach ensures gradual, sustainable chest fat reduction, fostering better health and body composition.
Misconception Around Chest Fat
- Spot Reduction: You can’t target fat loss in specific areas like the chest through exercises alone. Fat loss occurs throughout the body as a result of overall calorie deficit, not just in the targeted area.
- Only an Issue for Overweight Individuals: Even individuals with healthy BMIs can experience chest fat due to hormonal imbalances, genetics, or other factors.
- Exercise Alone Eliminates Chest Fat: While exercise is crucial, a balanced diet and overall lifestyle changes are also necessary for effective fat loss, including in the chest area.
- All Chest Fat is the Same: Different factors can lead to different types of chest fat, including gynecomastia (hormonal) and general fat accumulation.
- Surgery is the Only Solution: Surgery is an option for severe cases, but lifestyle changes and medical interventions can effectively reduce chest fat without surgical procedures.
Understanding these myths helps promote a realistic approach to managing chest fat through lifestyle changes, proper education, and evidence-based strategies.
HealthifyMe Suggestion
It is extremely important to remember that better heart health is dependent on a low amount of chest fat in the body. Excessive chest fat in men also tends to make them feel insecure and therefore it is vital to keep this under control. However remember this process will require a good amount of exercise, sleep and water intake along with a balanced diet rich in health protein and fibre. Please remember weight loss is difficult for a body and hence do not look for spot reduction or rapid weight loss. give your body the time it needs to adjust and adapt to your weight loss journey.
Conclusion
By taking proactive steps to manage chest fat, you’re not just enhancing your physical appearance but also nurturing your overall well-being. Embrace a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and prioritize stress reduction and quality sleep. Remember, each small effort contributes to significant change over time. Stay committed, and believe in your journey to a healthier and more confident you. Your dedication will sculpt not only your chest but also a happier, healthier life. Start today, and let your determination shape your success story.
Disclaimer: The purpose of this article is just to disperse knowledge and raise awareness. It does not intend to replace medical advice from professionals. For further information please contact our certified nutritionists Here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can targeted exercises help reduce chest fat?
Targeted exercises can help tone and strengthen chest muscles, but they may not directly reduce fat in that area. Overall fat loss through a combination of diet and exercise is more effective.
Are there specific workouts that can focus on reducing chest fat?
While there are chest-focused exercises, such as push-ups and chest presses, they won’t solely reduce chest fat. Full-body workouts and fat loss strategies are more effective.
What role does diet play in reducing chest fat?
Diet is crucial for fat loss. A balanced diet with a calorie deficit promotes overall fat reduction, including chest fat.
Is cardio exercise effective in reducing chest fat?
Yes, cardio exercises help burn calories and contribute to overall fat loss, including in the chest area.
Can strength training help with chest fat reduction?
Strength training boosts metabolism and muscle mass, indirectly aiding in fat loss, including chest fat.
How long does it take to see results when trying to reduce chest fat?
Results vary, but noticeable changes can take several weeks to months with consistent exercise and a healthy diet.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can aid in chest fat reduction?
Prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and avoiding excessive alcohol can support fat loss efforts.
Can hormonal imbalances contribute to chest fat accumulation?
Yes, hormonal imbalances, like high estrogen levels, can affect fat distribution, potentially leading to chest fat accumulation.
Are there any specific foods that promote chest fat loss?
No specific foods target chest fat. A balanced diet supports overall fat loss.
How does overall body fat percentage impact chest fat?
Lowering overall body fat through diet and exercise reduces fat accumulation, including in the chest area.
Can chest fat be reduced through non-surgical methods?
Non-surgical methods, like exercise and diet, are the most effective ways to reduce chest fat.
What are some common misconceptions about reducing chest fat?
Misconceptions include spot reduction, relying solely on exercises, and thinking certain foods directly burn chest fat.
Is spot reduction of chest fat possible?
Spot reduction is generally ineffective; overall fat loss is key.